 BBC
BBCPublic health bosses say they hope to start reducing restrictions “very quickly” on a 12-mile stretch of canals in the West Midlands following a toxic chemical spillage.
Sodium cyanide, which can cause seizures, vomiting and loss of consciousness, was confirmed on Tuesday as the chemical spilled into the waterway in Walsall.
People have been urged not to go near a long section of the canal network and towpaths from the middle of the borough to Birmingham and including connected waterways in Wednesbury, Tipton and West Bromwich.
The authority’s interim director of public health, Nadia Inglis, said they were “doing things cautiously but as quickly as we can”.

“We’re testing all points of that affected area currently and we’ll be reviewing those results as they come through,” Dr Inglis added.
“We’ll be removing those restrictions and hopefully reducing the size of that potentially affected area where we are confident there isn’t a risk to health.”
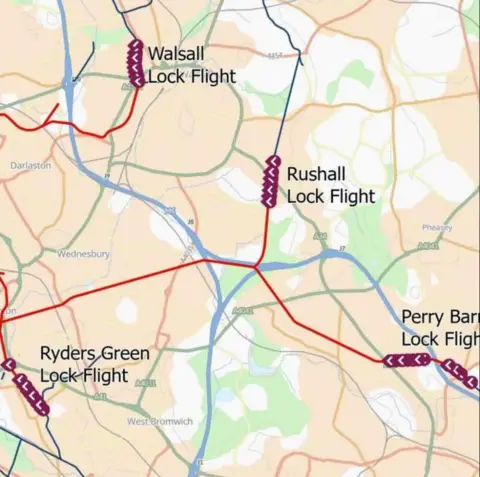
The exclusion zone markers run from the Walsall lock flight to lock flights at Rushall/Ryders Green in the borough and Perry Barr in Birmingham.
 Walsall Council
Walsall CouncilSodium cyanide dissolves in water and can have serious adverse health effects if people or pets come into direct contact with it, the council advised.
Anyone exposed to the water who felt unwell should seek medical advice through the NHS 111 service or phone 999 in an emergency, a spokesperson for the authority added.
People living on boats on the canal in the affected area were being made aware of the spill, the Canal and River Trust said.
Dr Inglis added: “Our primary aim has been to keep the public safe and to protect their health and wellbeing.
“Given the nature of the substance, we’re taking a cautious approach to protecting our public until we know it’s safe to open those canal towpaths again.”

What is sodium cyanide?
- The chemical sodium cyanide is a white crystal-like solid with a faint almond odour
- It is used in industry for metal cleaning, plating and extraction
- When cyanide salts are swallowed they release cyanide in the body – they can also be absorbed through the skin
- Expose can cause symptoms including headaches, nausea, dizziness, loss of consciousness, seizures and vomiting
- It can be rapidly fatal if inhaled or ingested as it interferes with the body’s ability to use oxygen
(Source: UK Health Security Agency)
Dr Delia Garratt, chief executive of Birmingham and Black Country Wildlife Trust said the spillage would have a devastating impact on wildlife.
She added she hoped those responsible would face the full force of the law.
“Environmental watchdogs must be empowered and sufficiently resourced to ensure they can monitor and inspect polluters, and enforce penalties upon those who break the law.”




